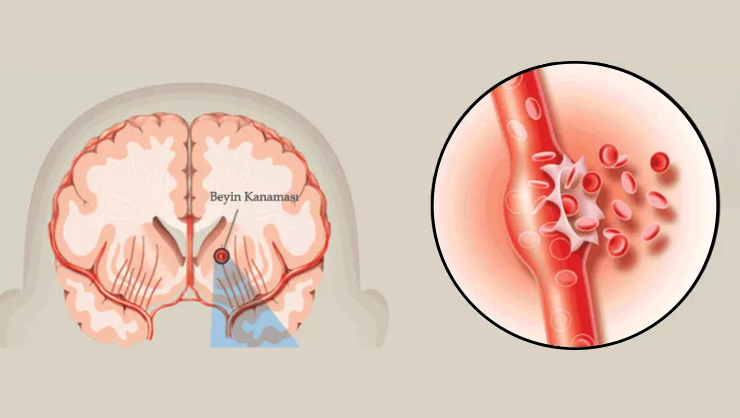
Brain Hemorrhage
It is the death of brain cells in the brain tissues close to the hemorrhage due to bleeding in the brain vessels. The death of brain cells causes loss of function in the affected area of the brain. A brain hemorrhage can cause a stroke, commonly known as a stroke. Brain hemorrhages account for about 13 percent of strokes.
How does a brain hemorrhage occur?
When blood from a ruptured brain vessel irritates brain tissues, it causes swelling of the tissue. This swelling is known as cerebral edema. The blood collects in a type of blood clump called a hematoma. The edema and hematoma increase the pressure on the brain tissue in the immediate area. This pressure reduces blood flow to that area of the brain. Brain cells that cannot be supplied with enough blood die permanently. Cerebral hemorrhage can occur in the brain tissue, between the brain and the membranes covering it, between the layers of the membranes of the brain, between the outer cerebral membrane and the brain bone.
Causes of brain hemorrhage
● Head trauma, injury: For people under 50 years of age, it is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain.
● High blood pressure: If left uncontrolled, this chronic condition weakens the blood vessels in the brain over a long period of time. If left unchecked, high blood pressure can lead to brain aneurysms and cerebral hemorrhage.
● Aneurysm: It is the formation of a bubble as a result of weakening of the blood vessel in the brain. Over time, it can burst the weakened blood vessel and cause cerebral hemorrhage and stroke. It is the main preventable cause of brain hemorrhages.
● Blood vessel abnormalities: Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth as an abnormality.
● Some liver diseases
● Brain tumor
● Genetic predisposition
● Drug and stimulant use
● Smoking and alcohol use
What are the Symptoms of a Brain Hemorrhage?
Symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary. What the symptoms are depends on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the bleeding and the amount of tissue affected.
Symptoms can develop suddenly or over time. They can get progressively worse or appear suddenly.
Any of the following symptoms may indicate a brain hemorrhage. This is a life-threatening situation and the patient should contact the emergency room immediately.
● Sudden severe headache
● Seizures in people with no previous history of seizures
● Weakness in an arm or leg, inability of a part of the body to perform its functions
● Nausea, vomiting, taste disturbance
● Changes in vision, spontaneous movement of the eyes
● Tingling or numbness in the body
● Difficulty speaking or understanding what is being said
● Difficulty swallowing
● Reading difficulties
● Loss of fine motor skills such as writing, trembling
● Loss of coordination and balance
● Loss of consciousness
● Sleepiness, inability to react to stimuli in the environment.
On the other hand, many of these symptoms can often be caused by conditions other than a brain haemorrhage.
Brain Hemorrhage Treatment
Treatment of bleeding in the brain depends on the location, cause and extent of the bleeding. Surgery is often required to relieve swelling and prevent bleeding. After any head injury, the patient should not be kept asleep for 24 hours to determine whether a brain hemorrhage has occurred. This is because a brain hemorrhage may have started, but may not show any symptoms at first. The aim of brain hemorrhage treatment is to eliminate the cause of the bleeding.
Patients with a brain hemorrhage are treated in intensive care units. The patient's recovery time depends on the location and severity of the bleeding in the brain, The characteristics of the surgical intervention varies according to the patient himself/herself, his/her age and resistance. Therefore, it is not possible to give clear data.
Some patients recover completely. Possible complications include stroke, reduced or lost brain function, side effects from medicines or treatments and loss of the patient. A brain hemorrhage is a serious health problem. Even if all possible treatment methods are successfully applied, the patient may die. On the other hand, patients recovering from a brain hemorrhage need a certain period of time to determine whether the loss of function is permanent. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are often recommended for these patients.
Can Brain Hemorrhages Be Prevented?
Preventing brain hemorrhage is possible by eliminating the factors that cause brain hemorrhage.
First of all, patients with high blood pressure must be treated and their blood pressure must be under control. Studies show that approximately 70 percent of cerebral hemorrhage patients have a history of high blood pressure. Therefore, patients with high blood pressure should monitor and control their blood pressure with diet and blood pressure medications.
Smoking and drug use should be stopped.
Rules must be followed when driving and seat belts must be worn to prevent head trauma.
Patients with a family history of aneurysm should definitely be investigated for aneurysm if they also have symptoms of the disease.
Patients with an aneurysm, also known as a bubble in the brain, should definitely be treated.
For information and treatment, you can contact Associate Professor Dr. Ali Yilmaz here.